Process optimization is crucial in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving performance. Whether refining chemical processes or improving power generation cycles, the ability to fine-tune operational parameters leads to significant benefits. This article explores how process optimization works, its applications in process simulation, and how to set up and evaluate optimization projects.
Use-Cases for Optimization in Process Simulation
Process simulation involves creating a mathematical model of a system to analyze its behaviour under different conditions. Optimization takes this further by determining the best design or operating conditions based on predefined objectives. Some common use cases include:
- Power Plant Efficiency: Optimizing steam cycle parameters to maximize power output while minimizing fuel consumption.
- Chemical Processes: Adjusting reaction conditions to improve yield and reduce waste.
Process simulation allows engineers to test different scenarios before implementing changes in real-world operations.
Preparing the Process Optimization
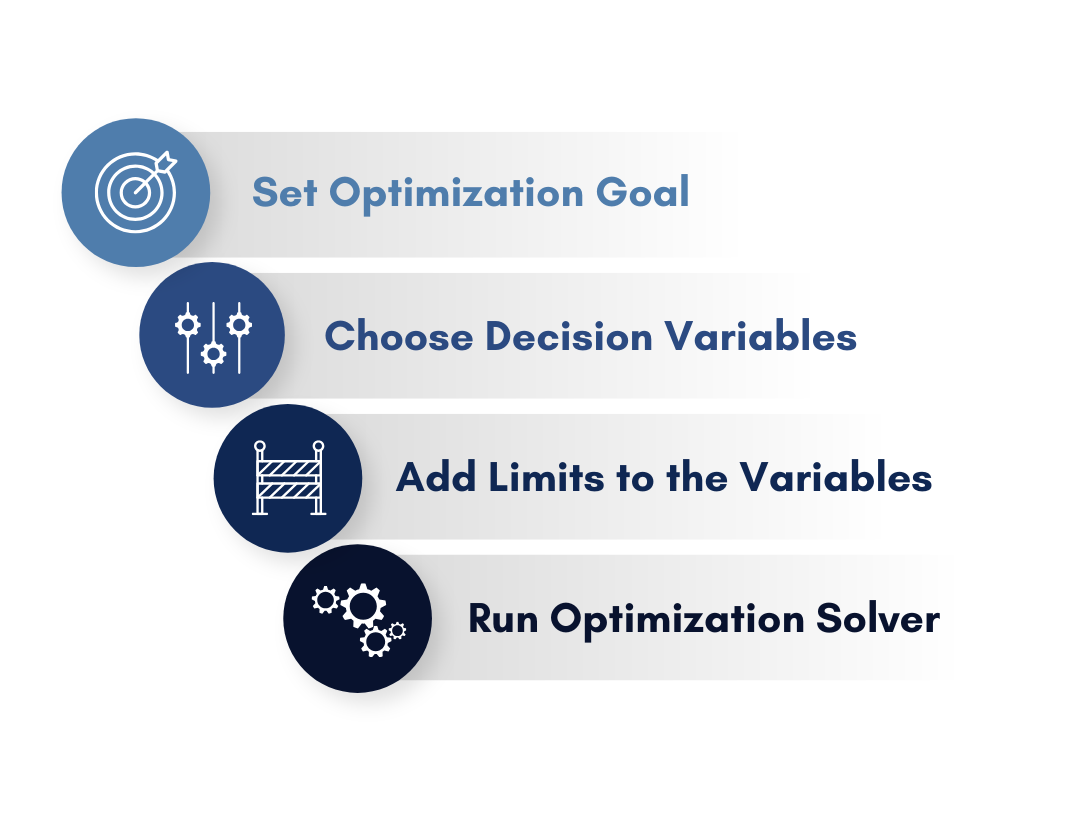 The 4 steps envolved when optimizing an existing process.
The 4 steps envolved when optimizing an existing process.
Before starting an optimization project, ensuring the simulation model is well-defined and converges properly is crucial. The key steps include:
- Defining the Optimization Objective: Determine which metric should be minimized or maximized.
- Configuring Decision Variables: Identify the parameters that can be adjusted to achieve the optimization goal.
- Establishing Constraints: Set limits to selected variables to ensure realistic solutions.
- Choosing an Optimization Method: Genetic algorithms, gradient-based solvers or other techniques are used to solve the optimization problem.
These steps provide the foundation for a successful optimization process.
Optimization Results
Once an optimization run is completed, the results must be carefully analyzed. The optimal solution found is based on the given constraints and model assumptions. However, engineers must validate the results by:
- Checking Convergence: Ensuring the process model reaches a stable solution.
- Interpreting the Outcome: Verifying that the optimized values make sense in real-world scenarios.
- Fine-Tuning Parameters: Running additional optimizations with refined constraints if necessary.
Process optimization can significantly save time and identify solutions which would have been overseen otherwise, but human expertise is always required to validate and implement the results effectively.
Optimize Your Process with IPSE GO
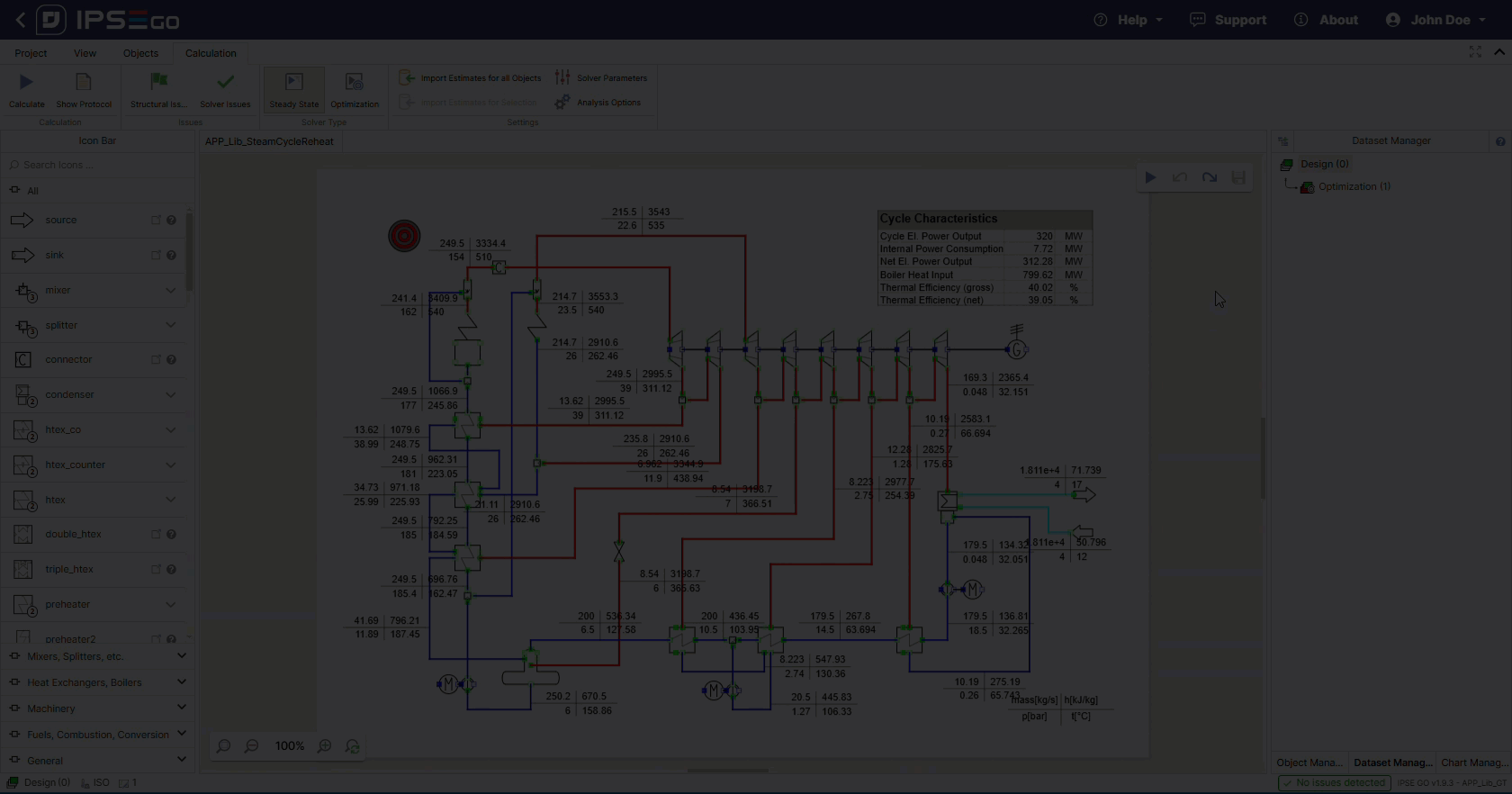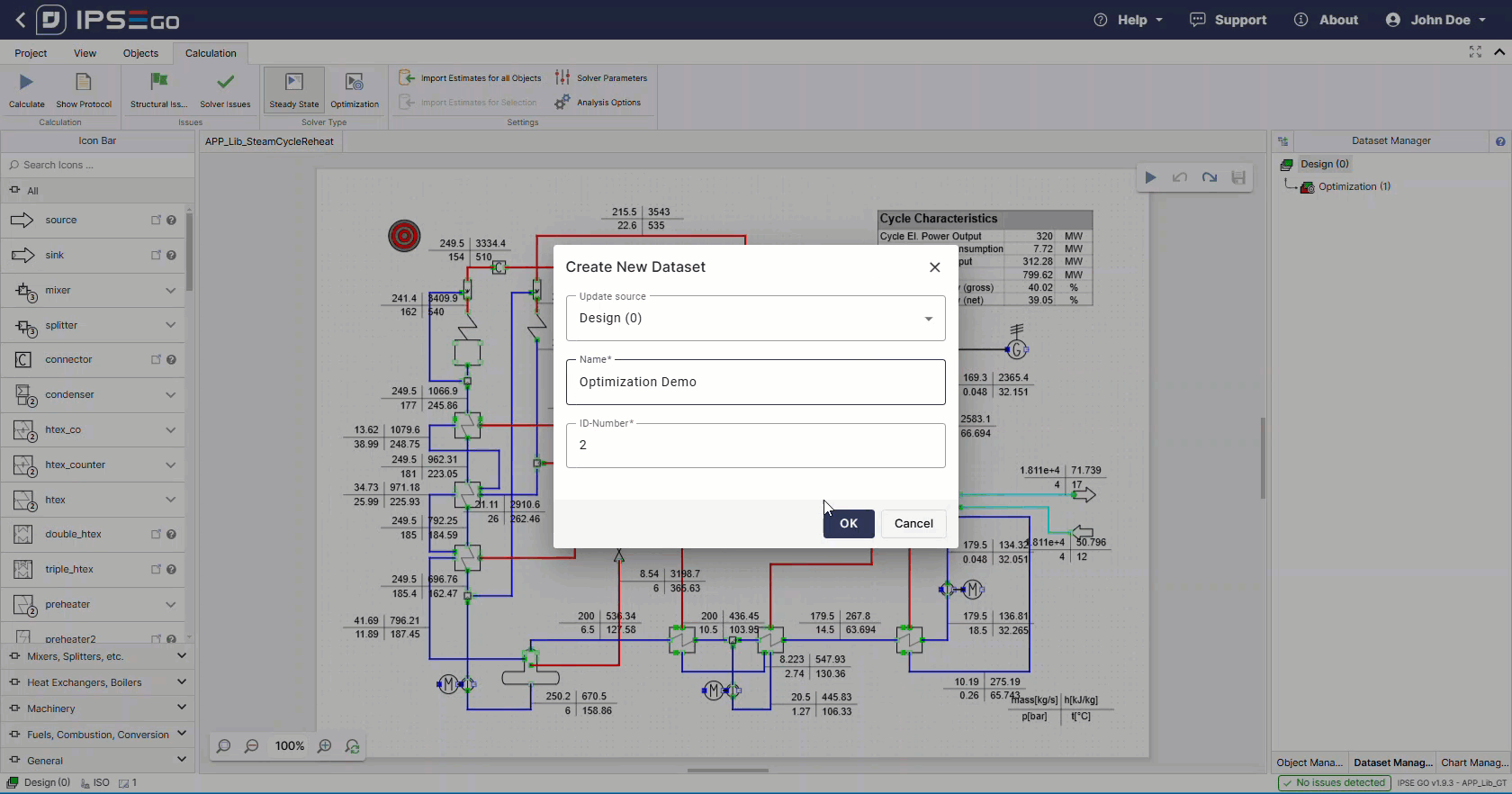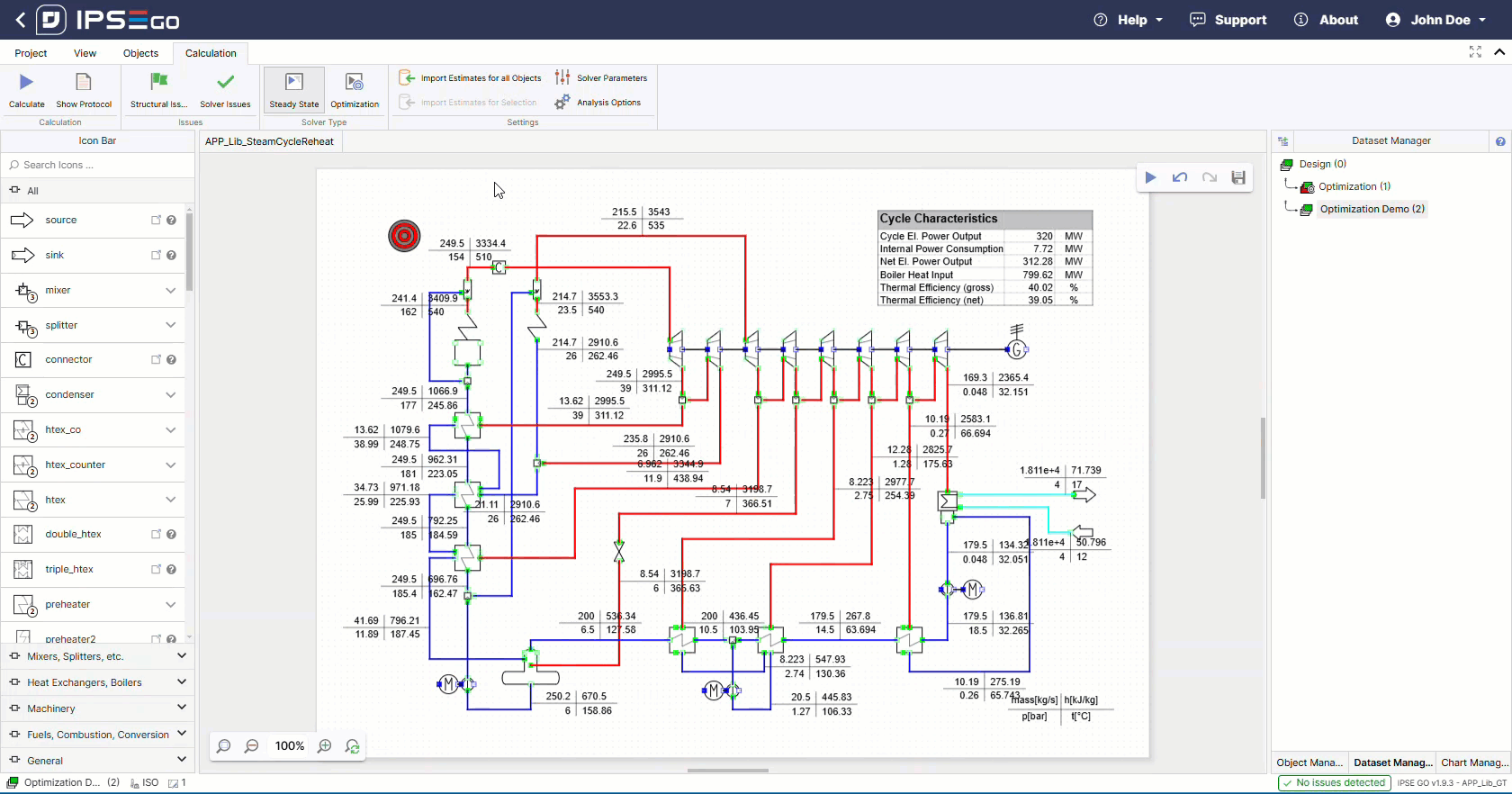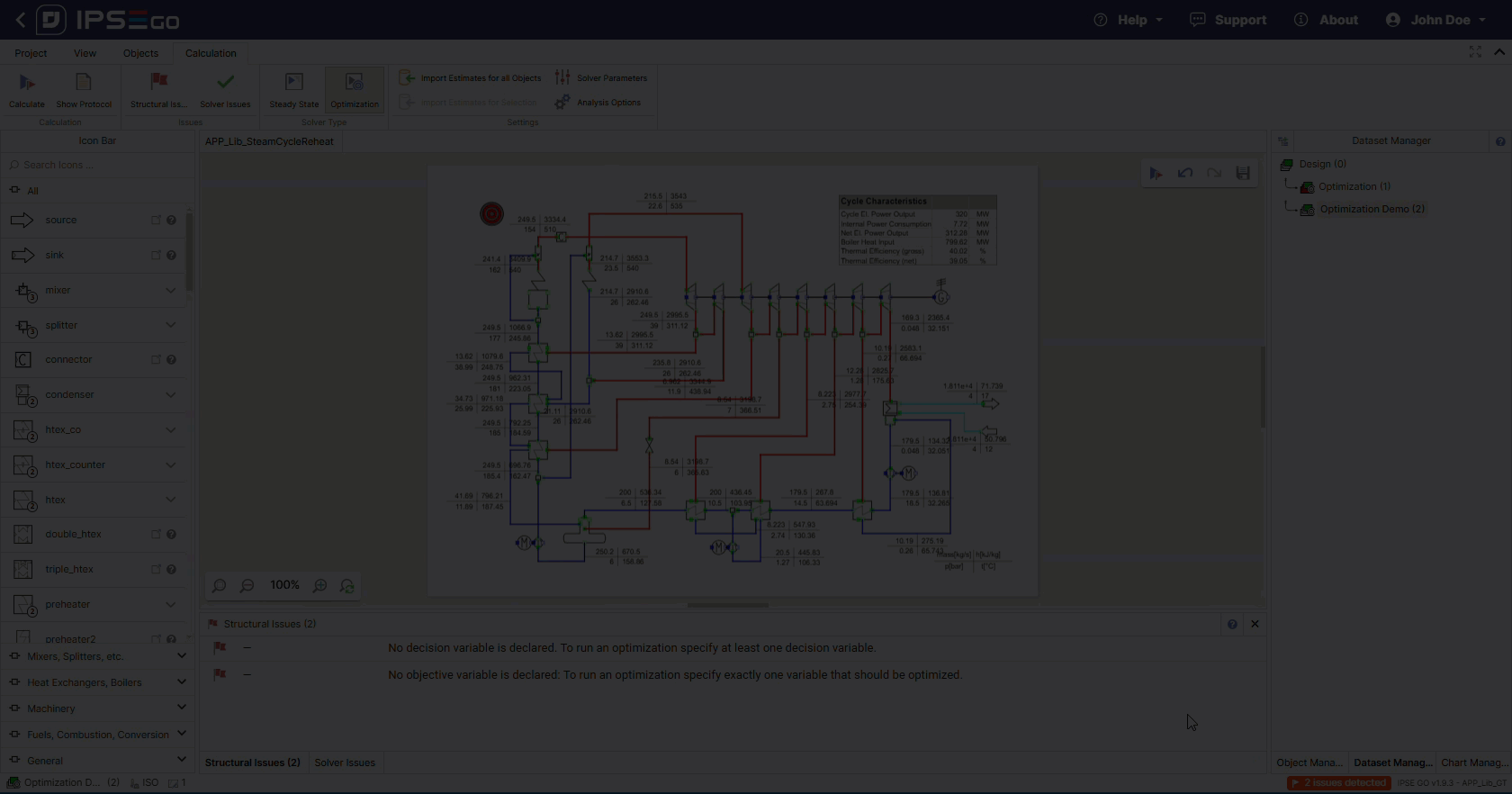 Create a new dataset with and select the optimization solver type for it.
Create a new dataset with and select the optimization solver type for it.
IPSE GO includes a dedicated module that can be used for optimization problems. Users can take their existing process model and by simply creating a second dataset optimize previously used parameters with ease.
The IPSE framework uses a custom-built genetic algorithm approach that efficiently solves for the best available solution as defined by the optimization parameters. Users can configure various solver-specific options including the number of generations used, the population size and mutation rates.
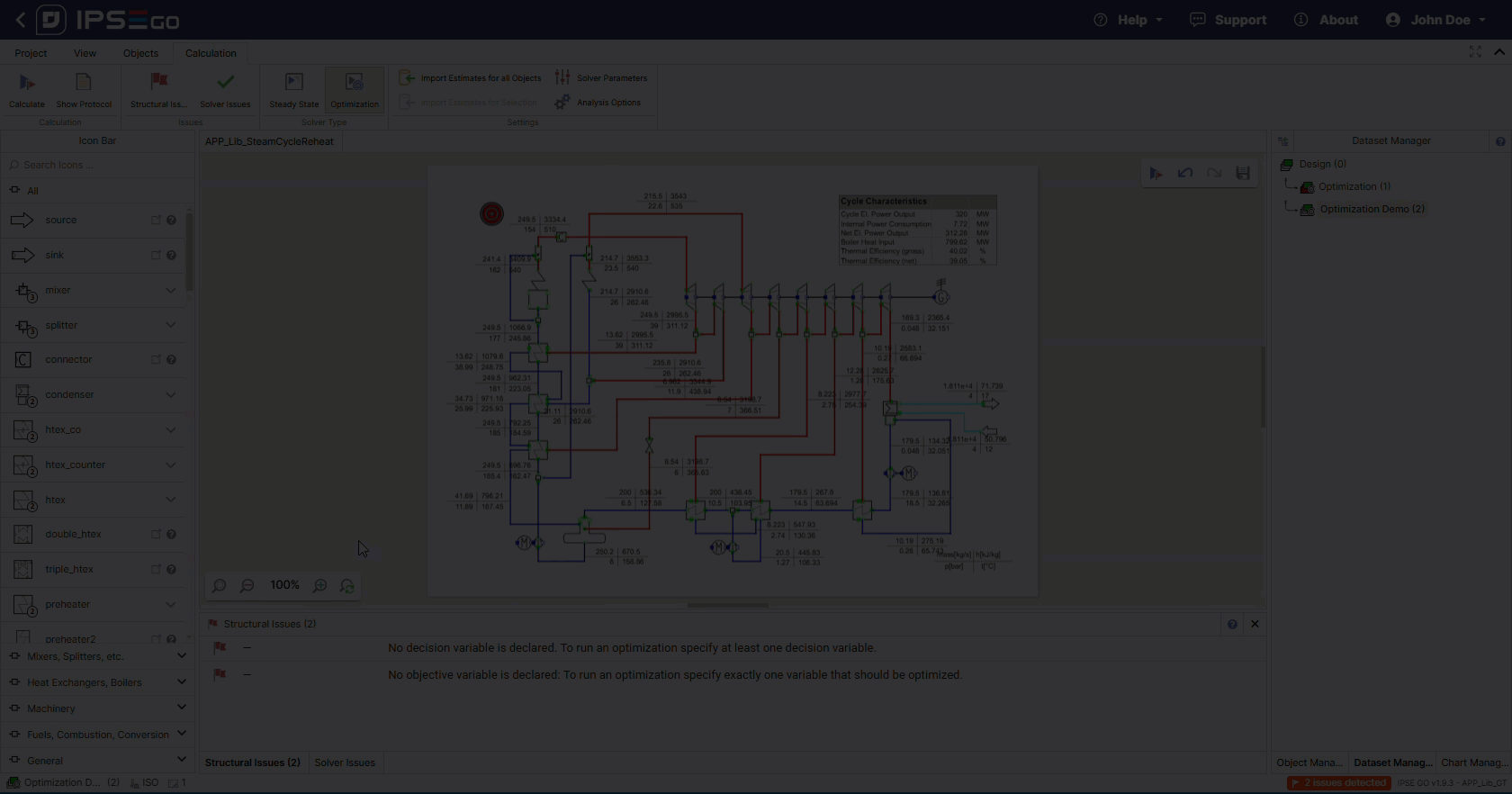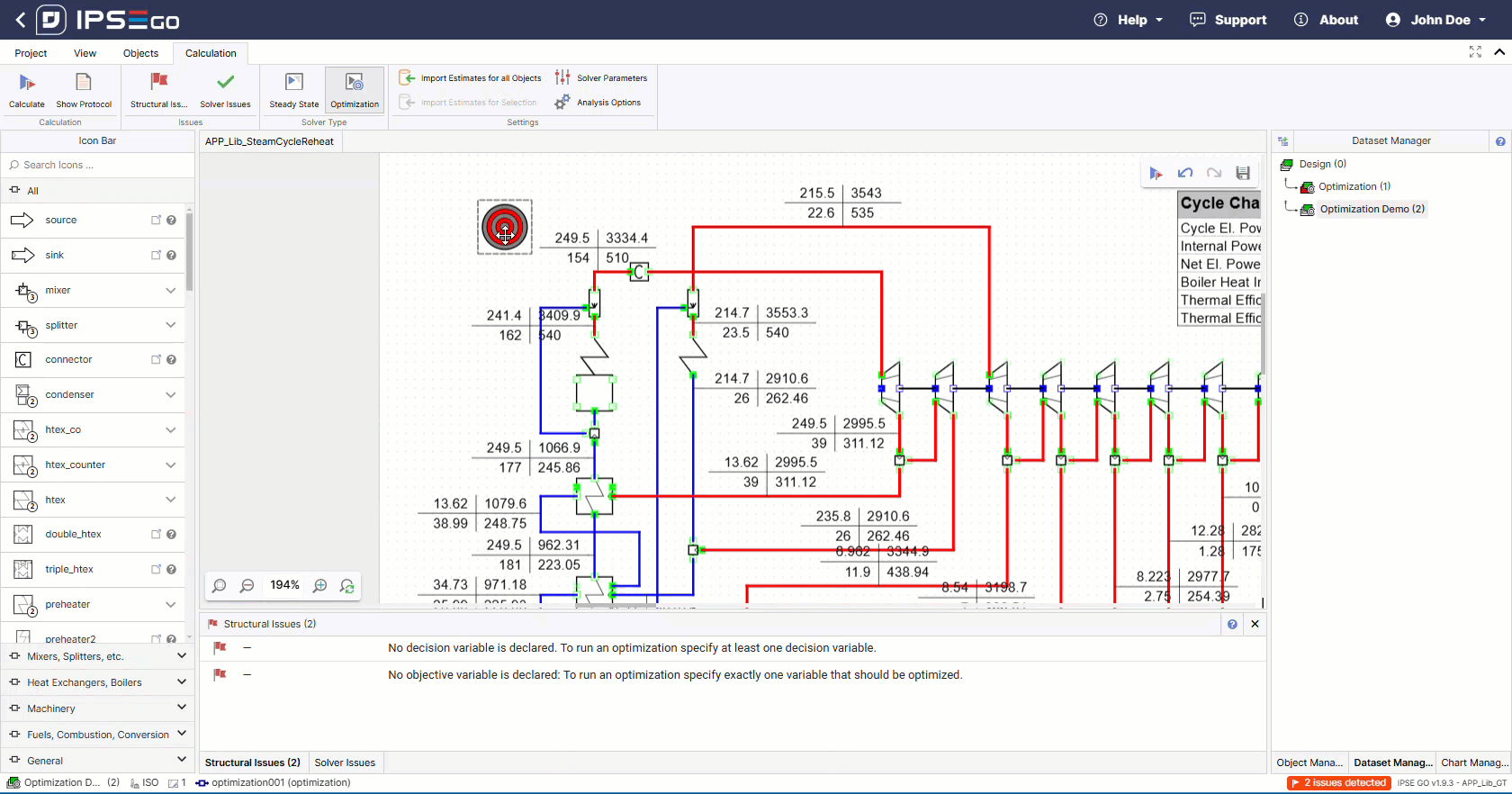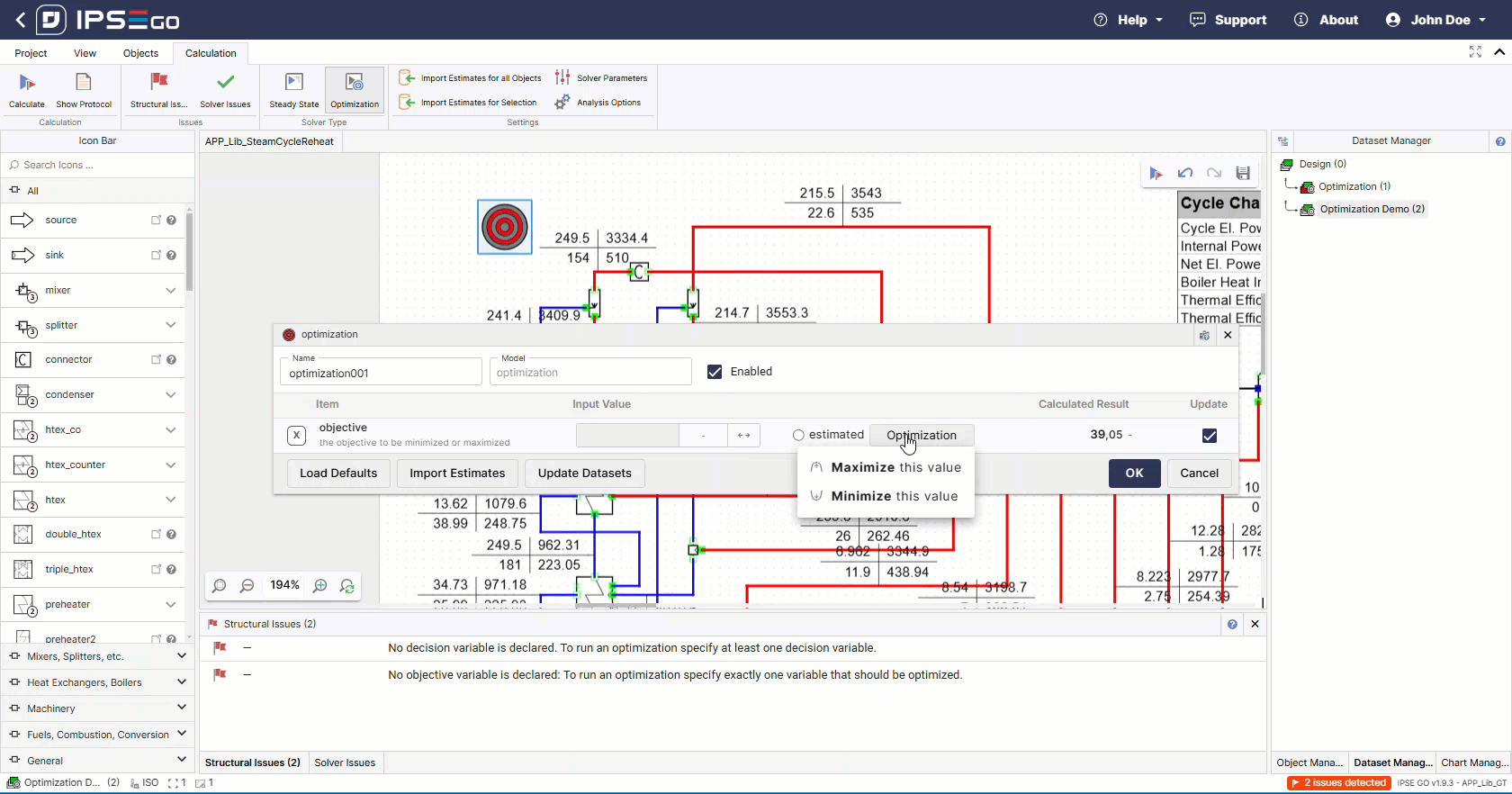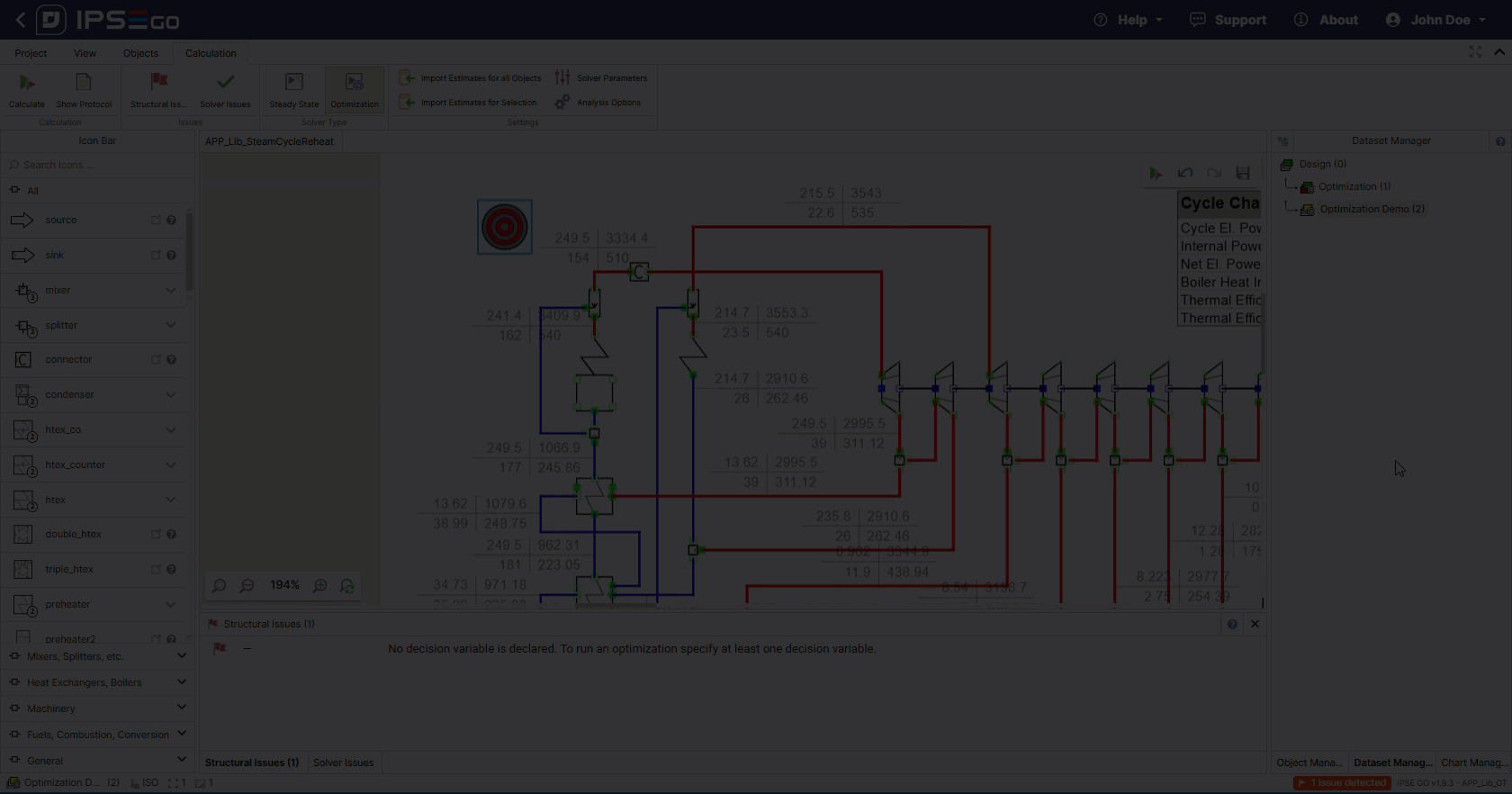 The optimization solver requires the selection of an optimization target.
The optimization solver requires the selection of an optimization target.
Setting up an optimization project follows the same steps outlined before. To begin, an optimization goal has to be defined. In IPSE, this can be a direct reference to an object variable or a free equation defined by the user.
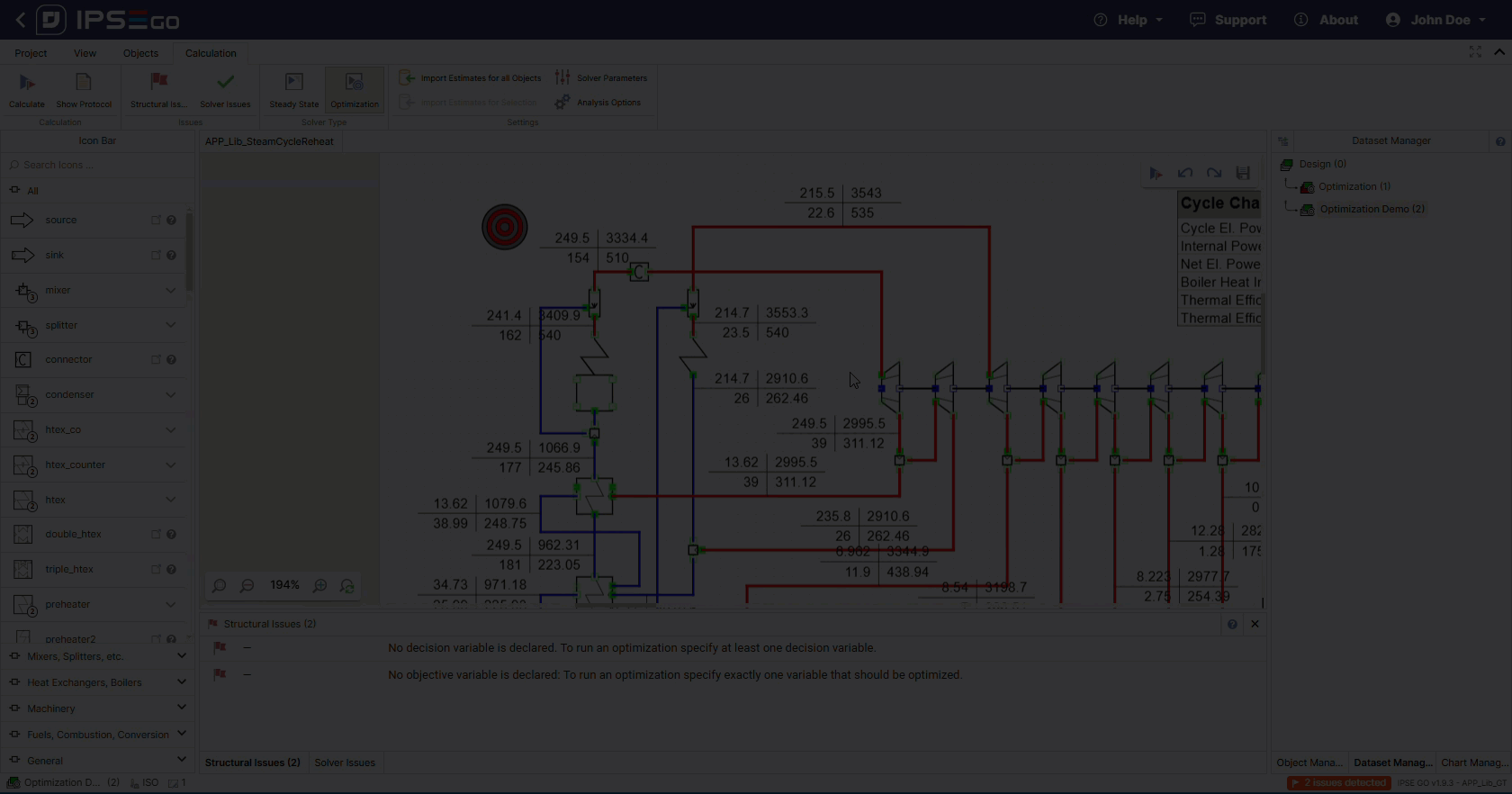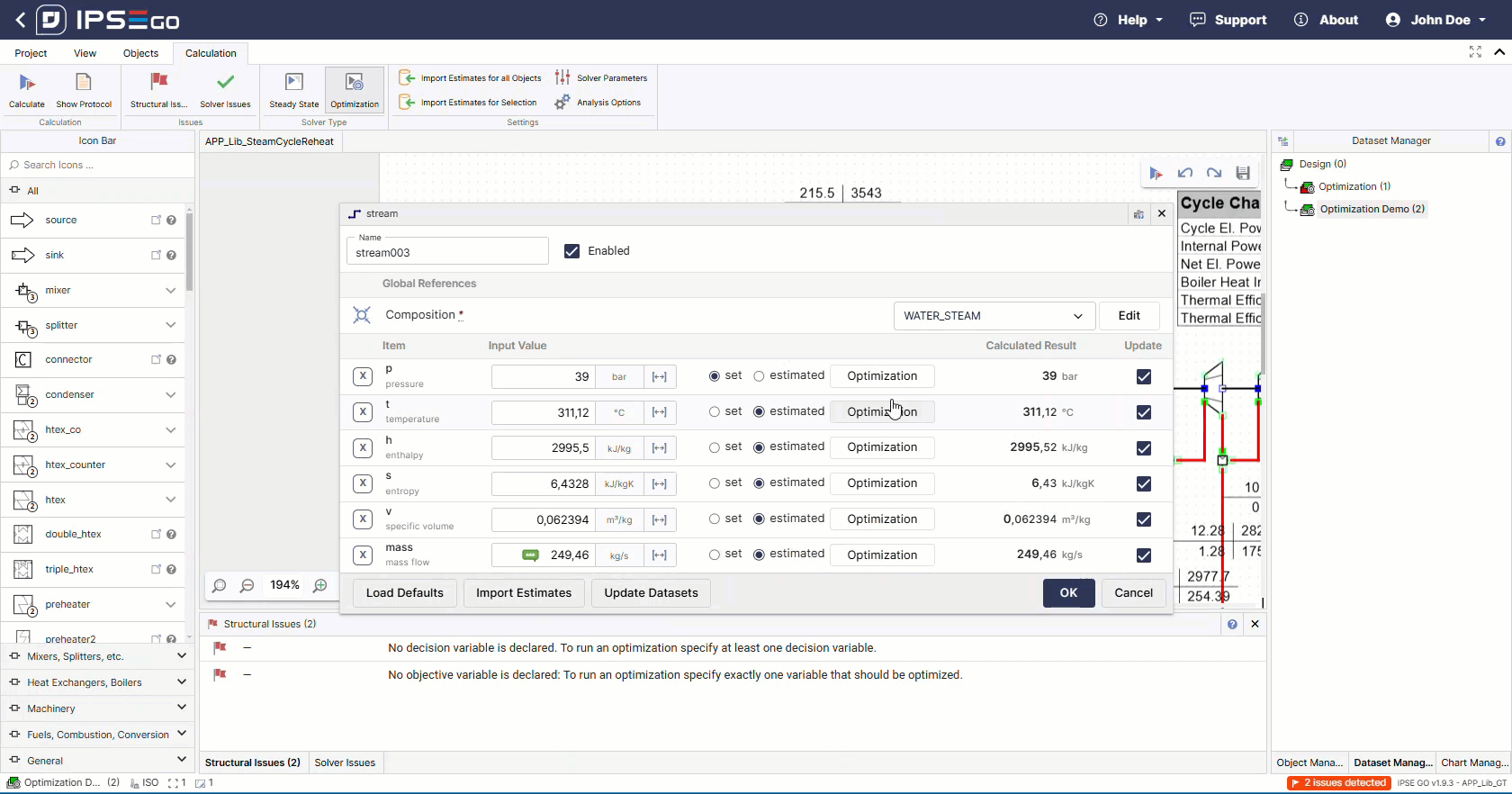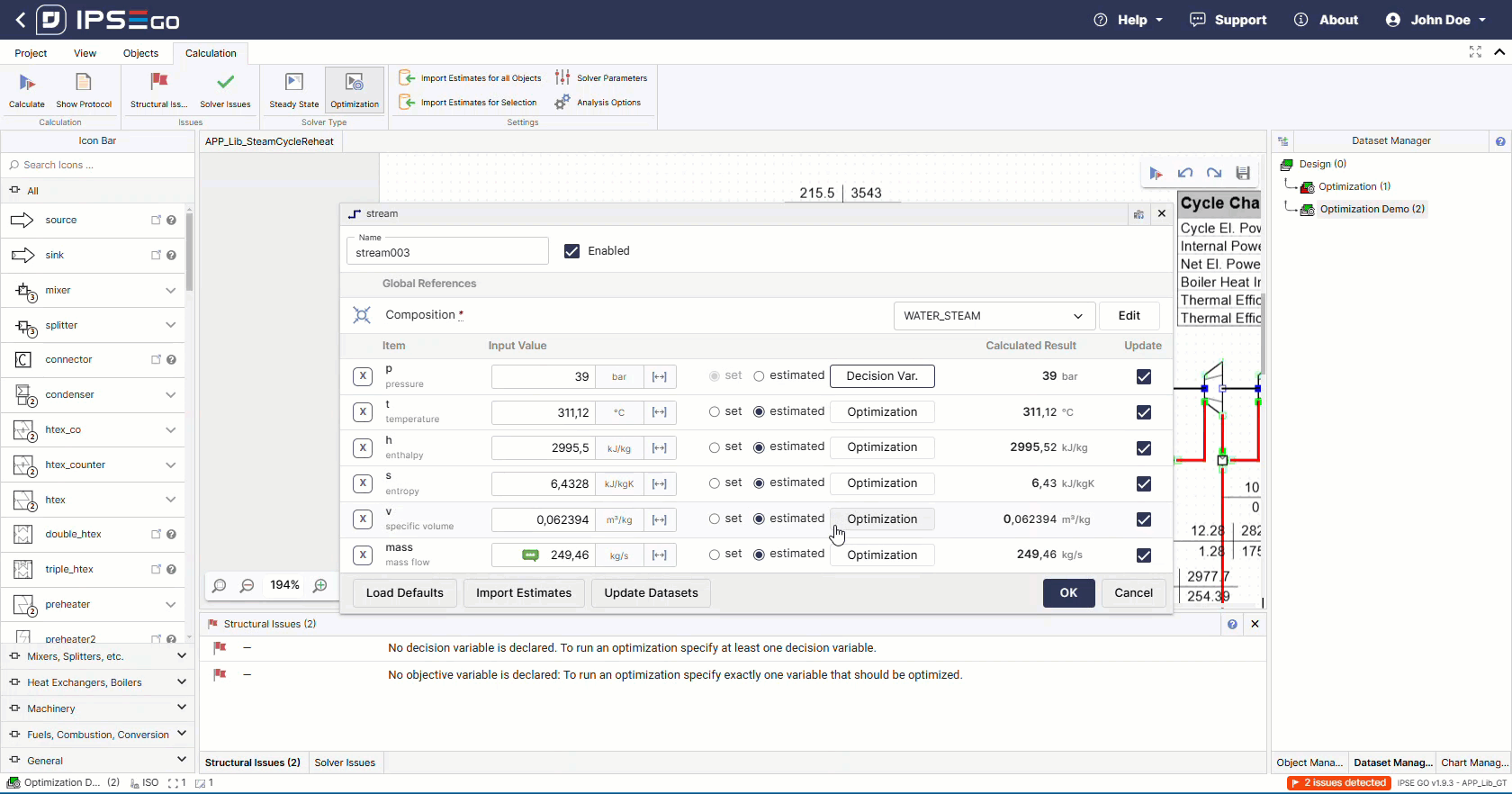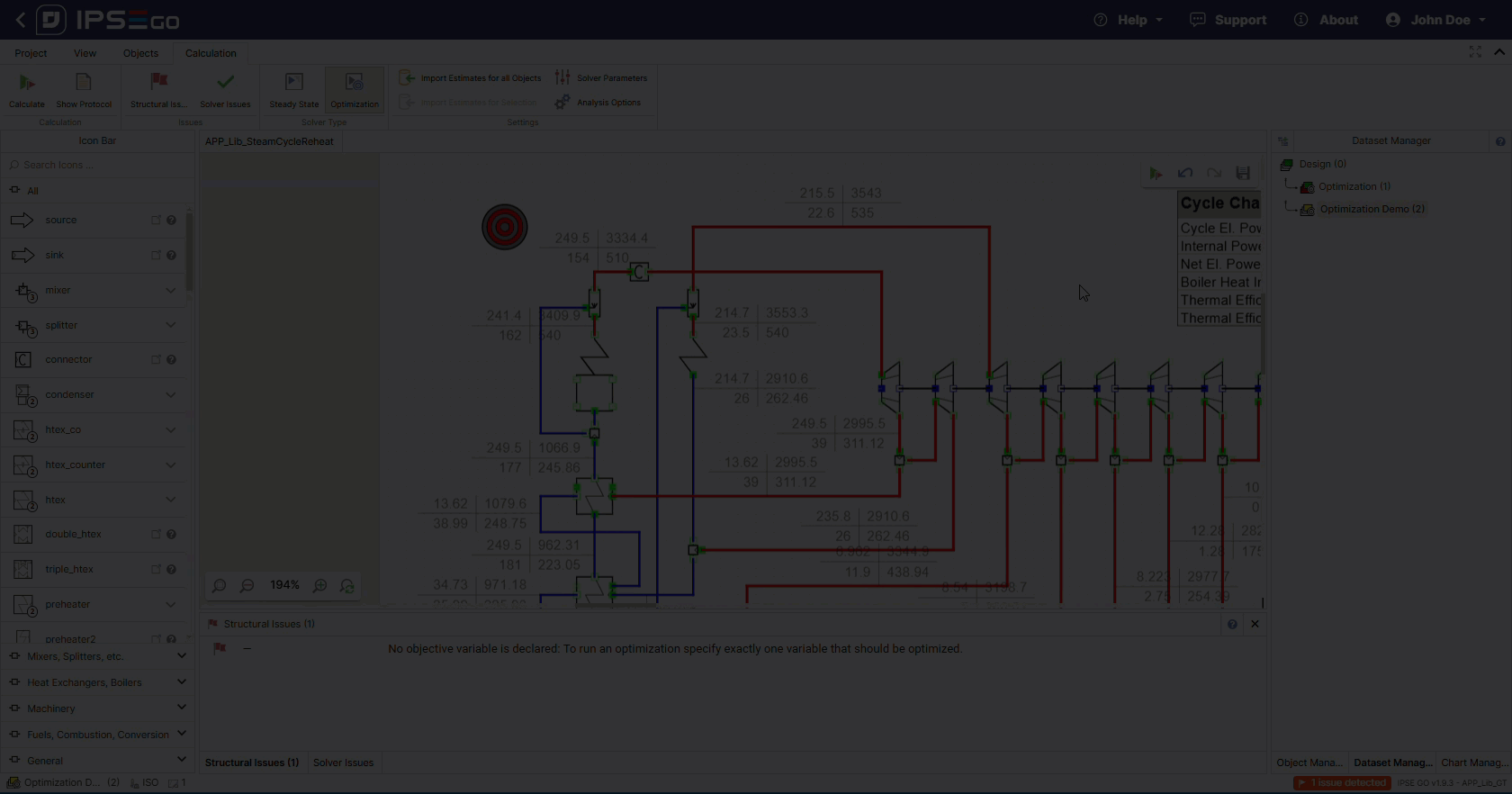 The solver also requires at least one configured decision variable.
The solver also requires at least one configured decision variable.
Secondly, the decision variables have to be chosen. The correct selection of decision variable has a direct impact on the optimization results. Decisions variables need to be limited as this defines the solution space. These limits can be changed and adapted further during optimization process development.
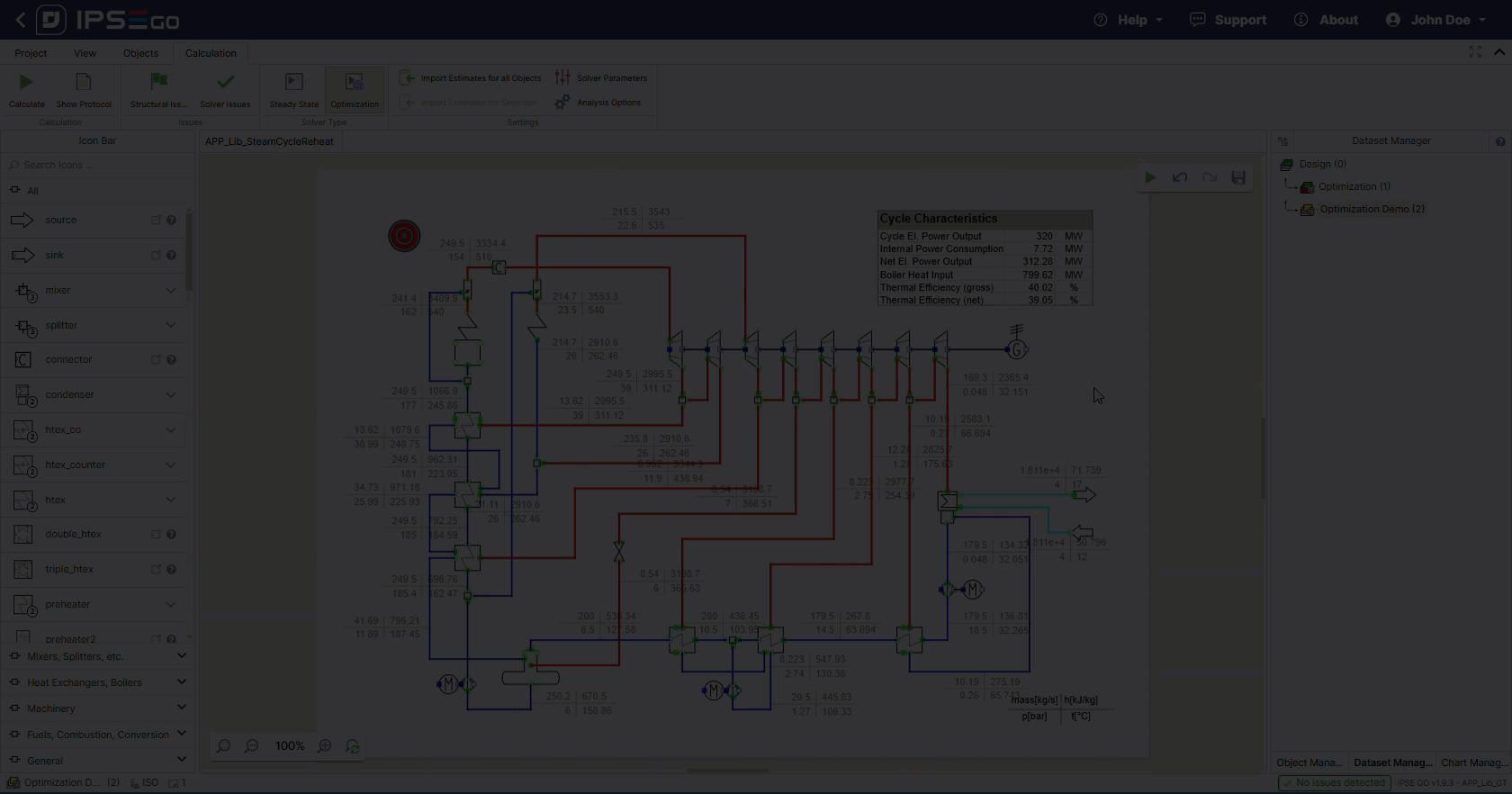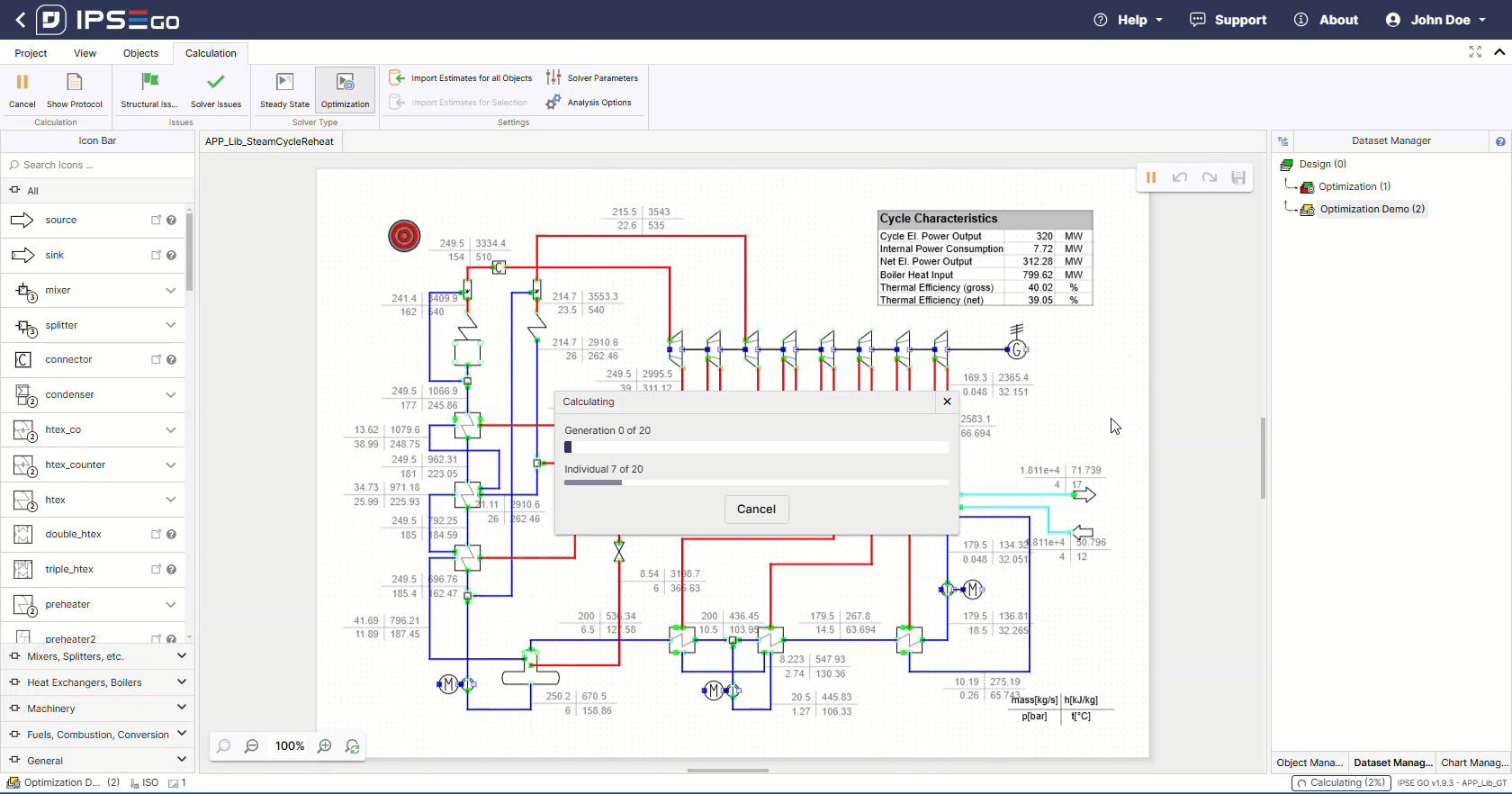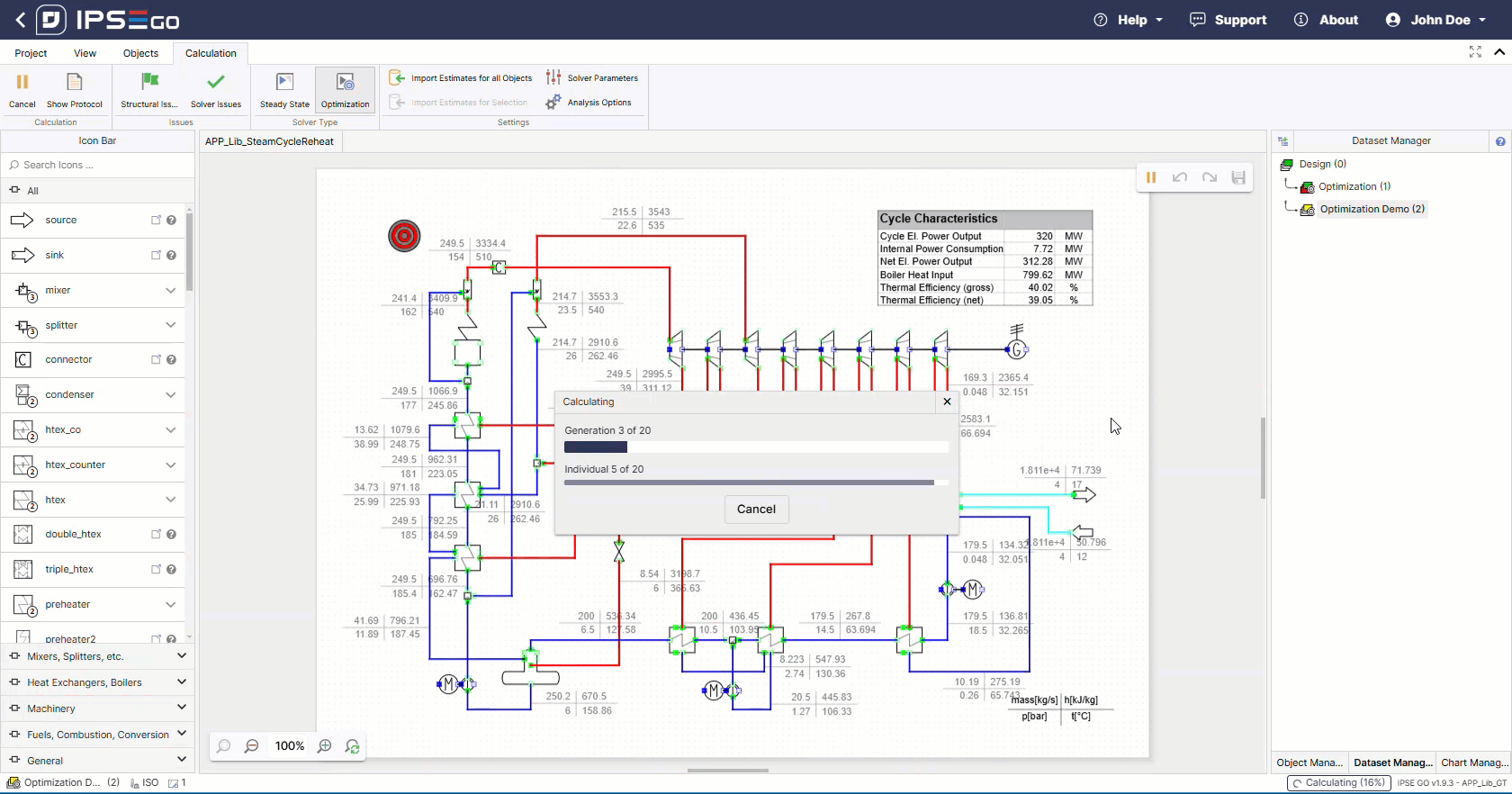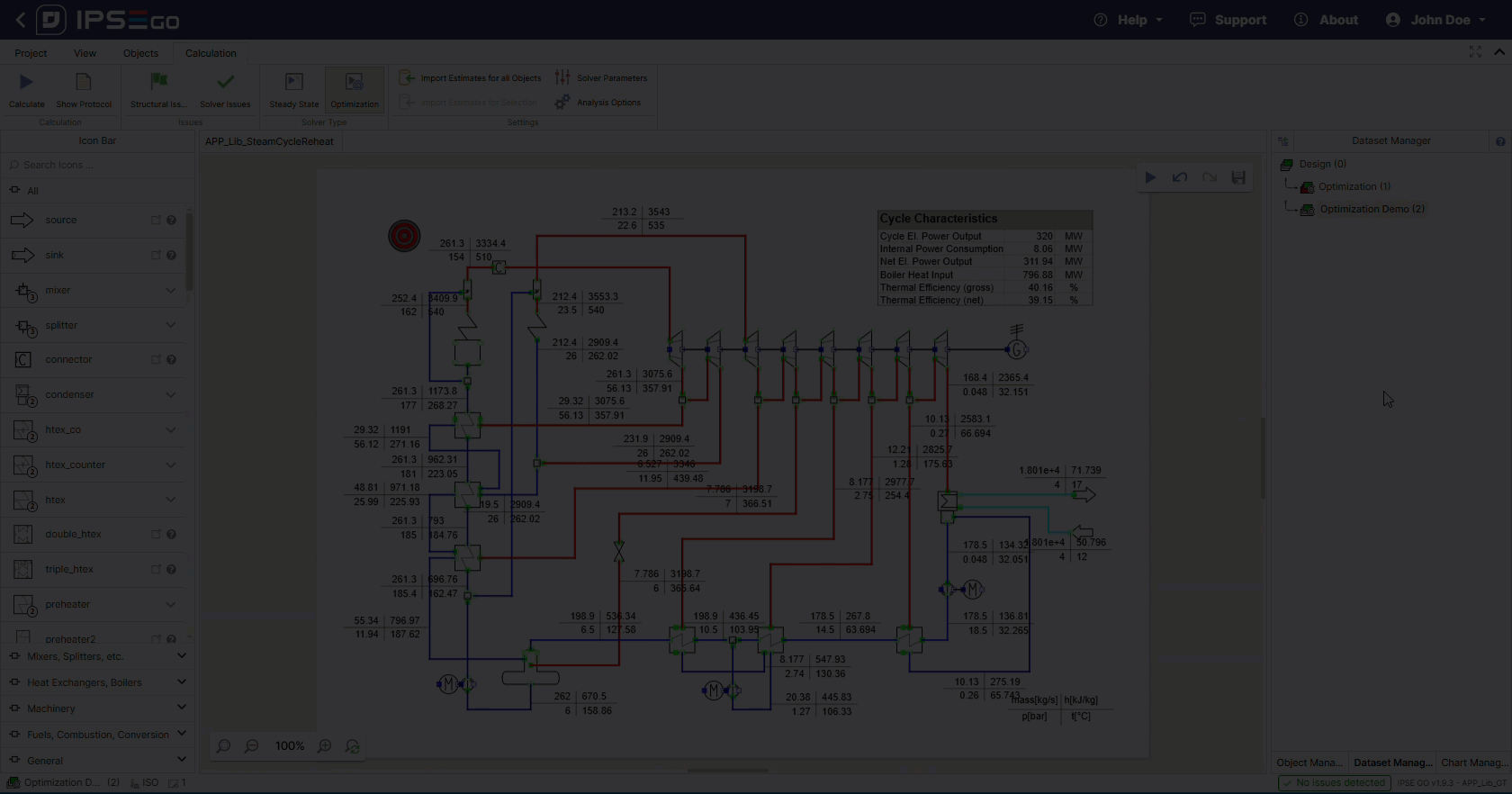 After successfull setup the optimization solver can be run.
After successfull setup the optimization solver can be run.
Similar to steady-state simulations the results of the optimization calculation are stored in the project and can be further used in IPSE GO for post-processing. This might include the displaying of charts, including values in data frames or simply printing the project with results on the flowsheet.
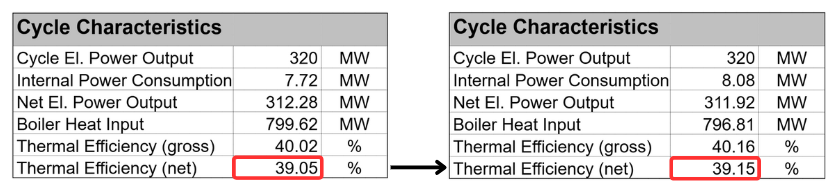 After a successful calculation the optimization target was successfully maximized.
After a successful calculation the optimization target was successfully maximized.
Conclusion
Process optimization is important in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving overall system performance. With the right approach, process simulation and optimization can lead to smarter, more efficient operations, driving innovation and sustainability in various industries. By leveraging tools like IPSE GO, engineers can systematically define optimization goals, select decision variables, and run advanced solvers to find the best possible solutions.


1_thumbnail.png)

