Discover how model-based data reconciliation in IPSEpro and IPSE GO ensures the highest level of data accuracy for your plant's operations. Learn how advanced statistical methods can optimize performance, minimize errors, and support better decision-making. Unlock the full potential of reliable process data for more efficient and cost-effective plant management.
Ensuring Reliable Plant Data with Model-Based Statistical Methods
Accurate data is the foundation for effective decision-making in plant operations, whether in power generation, manufacturing, or other industrial settings. Reliable data is essential not only for monitoring plant performance but also for optimizing each operational process. Inaccurate sensor measurements can lead to errors in analysis and costly decisions. Tools like IPSEpro and IPSE GO use advanced model-based data reconciliation techniques to enhance data reliability, making sure sensor data is as accurate as possible.
Why Reliable Data Matters
Accurate sensor data drives decisions related to process optimization, performance monitoring, and safety assurance. Even minor deviations in sensor readings can lead to significant errors, impacting how engineers and managers understand plant operations. This makes sensor validation crucial for maintaining operational integrity. By validating data, the process ensures that sensor inaccuracies are corrected, leading to more informed decisions and improved plant efficiency.
What is Model-Based Data Reconciliation?
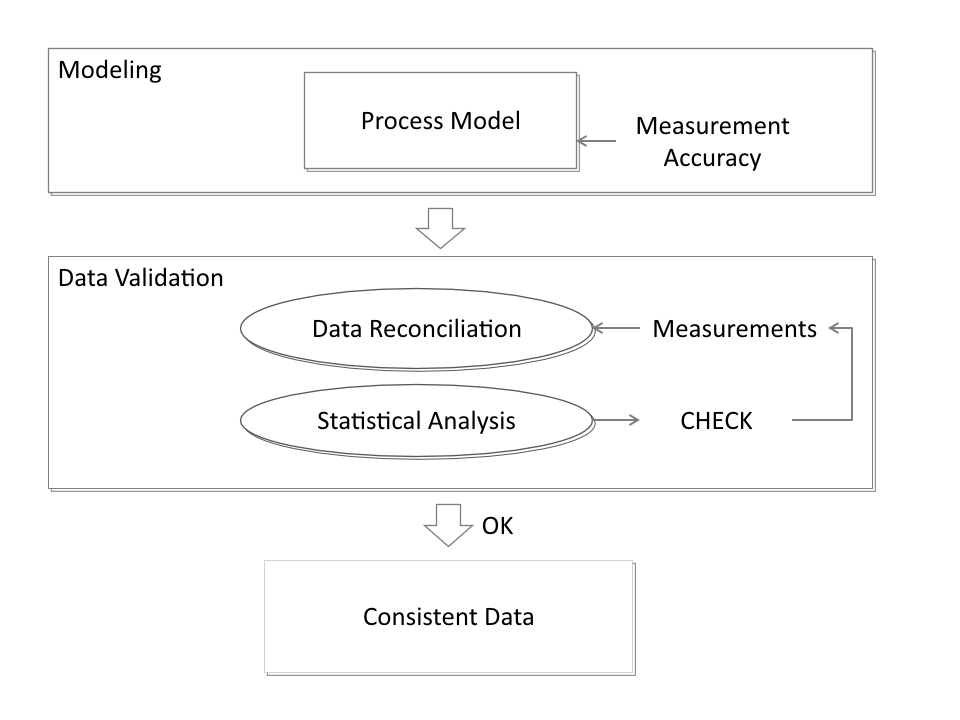
Data reconciliation is a statistical process that adjusts sensor data to fit the fundamental physical laws governing a process, such as mass and energy conservation. This method ensures that all data points are consistent and correct, providing the most accurate representation of the process.
The technique relies on having more data points than needed, creating redundancy. This redundancy enables the software to detect and correct inconsistent data. Through methods like the weighted least-squares criterion, data is fine-tuned, eliminating sensor errors. The result is a statistically validated, highly reliable dataset for further analysis.
The Versatility of IPSE for Data Validation
IPSE is a powerful simulation environment for building detailed process models. Engineers can represent every part of the plant, from turbines to heat exchangers, using unit operation models that accurately describe the physical behavior of components. Whether for simulation, optimization, or data reconciliation, IPSE’s flexible modeling capabilities ensure that the model can adapt to various needs with minimal effort.
Because IPSE models are equation-based, they can be tailored for multiple purposes. Whether you’re looking to simulate future conditions, optimize current processes, or validate sensor data, IPSE provides a consistent and robust framework.
Practical Data Validation with IPSE
Data validation in IPSE uses statistical assumptions, such as normal distribution, to create confidence intervals around adjusted sensor data. This allows engineers to identify and discard unreliable data points efficiently. If a statistical test fails, it could signal a problem with the data or even indicate an issue in the real-world process, like a leak or equipment failure.
The process repeats until the data is validated, ensuring reliability even when certain sensor data points are excluded. The ability to detect gross errors and missing data points is key to maintaining an accurate model.
Real-World Benefits of Data Reconciliation
Model-based data reconciliation provides a clear, consistent picture of a process’s state, reducing errors and improving decision-making. With IPSE, engineers can confidently rely on their data, leading to optimized process performance, fewer errors, and better overall efficiency. By integrating this method into regular operations, plant managers can reduce downtime, cut costs, and enhance the overall reliability of their plant.


_thumbnail.png)

1_thumbnail.png)